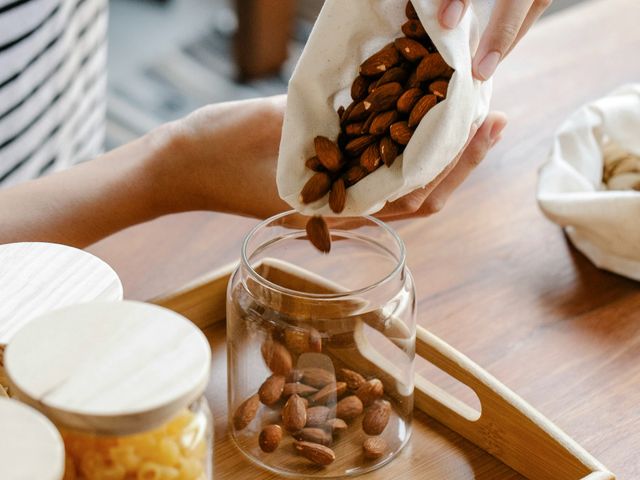
In recent years, there has been growing recognition of the role that magnesium plays in maintaining overall health, especially when it comes to cardiovascular well-being. Magnesium is a crucial mineral involved in numerous physiological functions, including muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and bone health. But one of its most significant roles may be its impact on heart health. This article delves into how magnesium influences cardiovascular health and how incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Understanding Magnesium’s Role
Magnesium is an essential mineral that is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. Its functions include regulating muscle contractions, nerve transmission, and maintaining a steady heartbeat. This mineral is also integral to the production of energy and the synthesis of proteins and DNA.
When it comes to cardiovascular health, magnesium helps maintain normal heart rhythm and is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. It works by relaxing the blood vessels, which can help prevent hypertension and reduce the workload on the heart. Additionally, magnesium supports the balance of electrolytes in the body, which is crucial for proper heart function.
The Connection Between Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease
Several studies have demonstrated a link between low magnesium levels and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Magnesium deficiency has been associated with various heart-related conditions, including hypertension, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Research suggests that adequate magnesium intake can help manage and reduce blood pressure levels. Magnesium helps relax blood vessels and improve endothelial function, which is vital for maintaining healthy blood pressure.
- Arrhythmias: Magnesium plays a critical role in maintaining normal heart rhythm. Deficiency in magnesium can lead to irregular heartbeats, or arrhythmias, which can increase the risk of more serious heart conditions. By ensuring sufficient magnesium levels, individuals may support their heart’s electrical stability and rhythm.
- Atherosclerosis: This condition involves the buildup of plaques in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow and lead to heart attacks or strokes. Magnesium may help prevent or slow the progression of atherosclerosis by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the cardiovascular system. If you are looking for some information about magnesium and heart health, you may visit health wellbeing to learn more.

Dietary Sources of Magnesium
Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet is an effective way to maintain adequate magnesium levels. Many foods naturally contain magnesium and can be part of a heart-healthy eating plan.
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of magnesium. These vegetables are also rich in antioxidants and other nutrients that support heart health.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds are high in magnesium. These foods also provide healthy fats and proteins, making them a heart-friendly snack.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are good sources of magnesium. They also offer fiber, which is beneficial for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are not only rich in magnesium but also provide protein and fiber. Including these in your diet can support overall cardiovascular health.
- Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel are high in magnesium and omega-3 fatty acids, both of which contribute to heart health.
- Fruits: Bananas and avocados are good sources of magnesium. They also provide other essential nutrients and can be easily incorporated into a variety of meals.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Magnesium-Rich Foods
To ensure you’re getting enough magnesium, consider the following tips:
- Diversify Your Diet: Include a variety of magnesium-rich foods in your meals. This not only helps you meet your magnesium needs but also provides a range of other nutrients that support heart health.
- Cook with Whole Ingredients: Opt for whole grains and fresh vegetables rather than processed foods. Whole foods are typically higher in magnesium and other beneficial nutrients.
- Snack Wisely: Choose nuts and seeds as snacks instead of processed options. They provide magnesium and healthy fats that support cardiovascular health.
- Plan Balanced Meals: Aim to include a source of magnesium in each meal. For example, add spinach to your breakfast omelet, include quinoa in your lunch salad, and serve salmon with a side of steamed vegetables for dinner.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help maintain magnesium balance in the body. Consider drinking mineral water, which can also contribute to your magnesium intake.
Conclusion
Magnesium plays a vital role in maintaining cardiovascular health by helping regulate heart rhythm, blood pressure, and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis. Ensuring adequate magnesium intake through a diet rich in leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, legumes, fish, and fruits can contribute to overall heart health and potentially reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Incorporating these magnesium-rich foods into your daily routine can be a simple yet effective strategy for supporting heart health. As with any dietary changes, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that your diet meets your individual needs and supports your overall well-being.