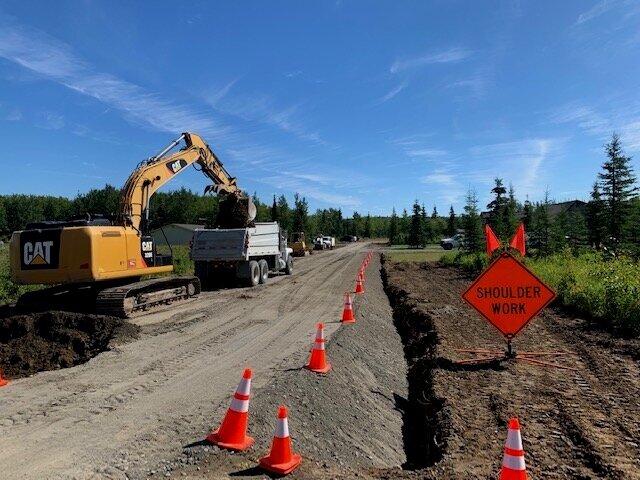
Road construction and maintenance are vital for transportation infrastructure, facilitating economic growth, mobility, and connectivity. However, the environmental impact of road work can be significant, posing challenges to ecosystems, biodiversity, and overall environmental health. To ensure sustainable development, it’s crucial to address these impacts proactively while implementing effective solutions.
Understanding the Environmental Impact
Road construction and maintenance activities can result in various environmental disturbances, including:
- Habitat Fragmentation: Roads can fragment natural habitats, disrupting wildlife corridors and migration patterns. This fragmentation can lead to isolation among populations, reducing genetic diversity and increasing the risk of species decline or extinction.
- Soil Erosion and Compaction: Excavation, grading, and compaction during road construction can degrade soil quality, leading to erosion and loss of fertility. Soil compaction reduces infiltration rates, exacerbating runoff and increasing the risk of sedimentation in nearby water bodies.
- Water Pollution: Runoff from roads and construction sites can carry pollutants such as sediment, heavy metals, and chemicals into rivers, streams, and groundwater. This pollution can degrade water quality, harm aquatic ecosystems, and threaten drinking water supplies.
- Air Pollution: Construction machinery and vehicles emit pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds, contributing to air pollution and respiratory health problems. Dust and emissions from unpaved roads can also impact nearby communities and ecosystems.
- Noise and Visual Disturbance: Road construction activities generate noise pollution, disrupting wildlife behavior and affecting nearby residents’ quality of life. Moreover, the visual impact of roads and associated infrastructure can alter landscapes and scenic vistas. Visit Line Marking Pro if you need more information or have any questions about the environmental impact of road work.

Addressing Challenges with Sustainable Solutions
While road work presents environmental challenges, various strategies and technologies can mitigate these impacts and promote sustainability:
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): Conducting thorough EIAs before road construction projects helps identify potential environmental risks and plan appropriate mitigation measures. EIAs consider factors such as habitat sensitivity, water resources, and air quality to inform decision-making and minimize adverse impacts.
- Green Infrastructure: Incorporating green infrastructure elements like vegetated buffers, permeable surfaces, and bio-swales into road design helps manage stormwater runoff, reduce erosion, and enhance habitat connectivity. Green infrastructure also improves air quality, mitigates heat island effects, and enhances aesthetic appeal.
- Wildlife Crossings: Building wildlife crossings such as bridges, tunnels, and culverts helps mitigate habitat fragmentation by providing safe passage for wildlife across roads. Strategic placement of wildlife crossings based on ecological data and animal behavior studies enhances connectivity and reduces wildlife-vehicle collisions.
- Erosion Control Measures: Implementing erosion control measures such as silt fences, sediment basins, and erosion blankets minimizes soil erosion and sedimentation during road construction. Vegetation restoration and revegetation efforts further stabilize slopes, reduce runoff, and enhance soil health post-construction.
- Low-Impact Construction Techniques: Adopting low-impact construction techniques like using recycled materials, minimizing land disturbance, and optimizing construction schedules reduces the environmental footprint of road projects. Employing efficient equipment, implementing dust suppression measures, and adhering to emission standards also minimize air and noise pollution.
Conclusion
The environmental impact of road work presents complex challenges that require holistic solutions and collaborative efforts from government agencies, developers, environmental organizations, and local communities. By integrating sustainability principles into road planning, design, and construction processes, we can mitigate adverse environmental effects, preserve ecological integrity, and foster resilient transportation systems for future generations.
Remember, every road we build today leaves an imprint on the environment tomorrow. Let’s pave the way for a sustainable future by navigating the environmental impact of road work responsibly and innovatively.